Jackson, Mississippi
Weather Forecast Office
How it Works
Prior to the dual polarization upgrade, the WSR-88D transmits and receives pulses of radio waves in only a horizontal orientation. As a result, the radar only measures the horizontal dimensions of targets (e.g. cloud and precipitation droplets). Dual-polarimetric radar transmits and receives pulses in both a horizontal and vertical orientation. As a result, the returning frequencies provide measurements of the horizontal and vertical dimensions of targets, supplying forecasters with better estimates of the size, shape, and variety of targets. The images below illustrate the difference between non-polarimetric radar and polarimetric radar.
Before Dual-Pol Upgrade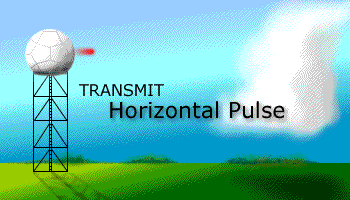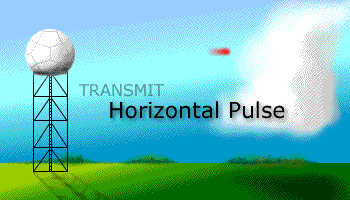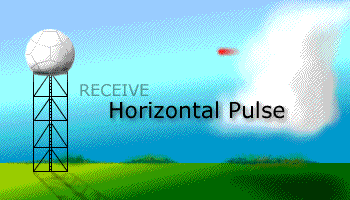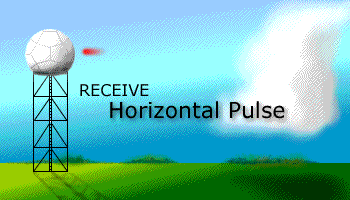 |
After Dual-Pol Upgrade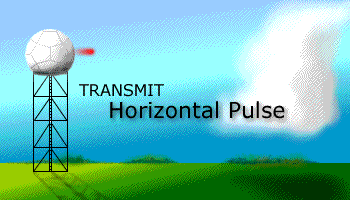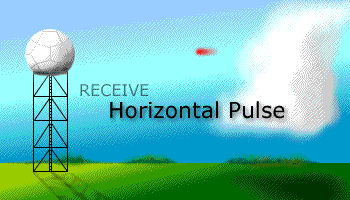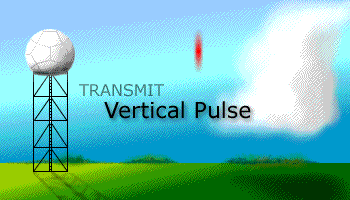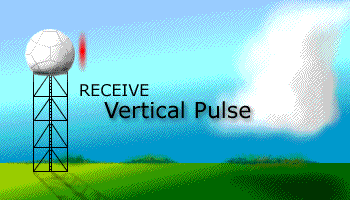 |
Here are some quick educational videos from NOAA Weather Partners.
This first video features Paul Schlatter explaining the difference between conventional Doppler radar and dual-polarized radar.
This next video takes a more comical approach to showing some of the benefits of the dual-pol upgrade.
Here are some of the benefits from the upgrade to dual-pol radar:
​For some real-life examples of ways that dual-pol technology has helped forecasters, check out the applications page.
US Dept of Commerce
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
National Weather Service
Jackson, Mississippi
234 Weather Service Dr.
Flowood, MS 39232
601-936-2189
Comments? Questions? Please Contact Us.


